Win a $15,000
Subscription to Approveit
Win a $15,000
Subscription to Approveit
Manual processes cost B2B companies up to 30% of their revenue.
Approveit helps you stop the loss by orchestrating workflows across all your tools in one place.
Manual processes cost B2B companies up to 30% of their revenue. Approveit helps you stop the loss by orchestrating workflows across all your tools in one place.



All you have to do to win a prize
is fill out the form
All you have to do to win a prize
is fill out the form
All you have to do to win a prize is fill out the form
We will randomly select a winner


Trusted by over 700 companies
Trusted by over 700 companies
Trusted by over 700 companies


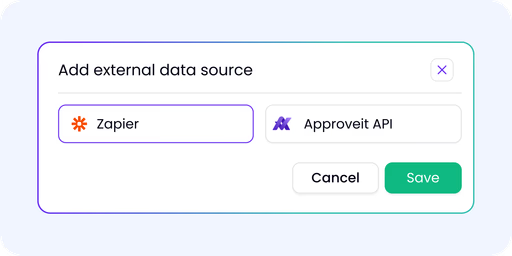
Connect workflows across your fools and teams


Integrate Slack, Microsoft Teams, ERPs, CRMs, and internal systems


Ensure full compliance with audit-ready logs and governance


Scale with REST APis.SOKs, and White label dions

Ensure full compliance with audit-ready logs and governance

Implement through REST API, SDKs, or White label integration
What You Get with Approveit?
What You Get with Approveit?
What You Get with Approveit?
Flexible workflow builder
Integration with favourite tools
Analytics and reports
Flexible workflow builder
Integration with favourite tools
Analytics and reports
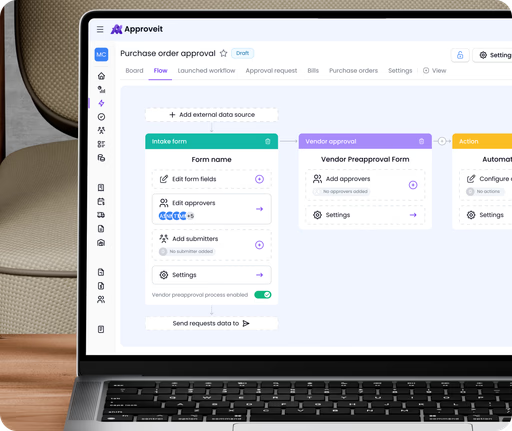

Flexible workflow builder
Integration
with favourite tools
Analytics and reports
Success Stories from Our Customers
Success Stories from Our Customers
Success Stories from
Our Customers

“Easy to use since it is directly integrated with Slack! We can also use third party integration to send the results to other softwares.”

Marcella Moniaga
CO-Founder and CCO at Astro

“It was very easy to set up, integrate into Slack, and configure workflows. Since it is integrated into Slack, all of the end users were able to start using it immediately with minimal training. A huge advantage vs a standalone approvals solution”

Andy Chimicles
Head of product at Blade

“Easy to select items necessary for creating work flows and it has a connectivity to other applications which broaden opportunities to make our business flow simple and effective”

Mariko Arai
Senior accountant at Midokura
“Easy to understand and implement with flexibility to adjust your structure. Improve the operation and communication among teams”

Danny L.
Finance manager at Easygo

“We love the way Approveit works within Slack, Its help us streamline our PTO and Expense requests. The support is amazing they seem to respond very quickly and were very helpful with the setup process”

Bobby G.
Executive pastor at Cape Christian

“Easy to use since it is directly integrated with Slack! We can also use third party integration to send the results to other softwares.”

Marcella Moniaga
CO-Founder and CCO at Astro

“It was very easy to set up, integrate into Slack, and configure workflows. Since it is integrated into Slack, all of the end users were able to start using it immediately with minimal training. A huge advantage vs a standalone approvals solution”

Andy Chimicles
Head of product at Blade

“Easy to select items necessary for creating work flows and it has a connectivity to other applications which broaden opportunities to make our business flow simple and effective”

Mariko Arai
Senior accountant at Midokura
“Easy to understand and implement with flexibility to adjust your structure. Improve the operation and communication among teams”

Danny L.
Finance manager at Easygo

“We love the way Approveit works within Slack, Its help us streamline our PTO and Expense requests. The support is amazing they seem to respond very quickly and were very helpful with the setup process”

Bobby G.
Executive pastor at Cape Christian

“Easy to use since it is directly integrated with Slack! We can also use third party integration to send the results to other softwares.”

Marcella Moniaga
CO-Founder and CCO at Astro

“It was very easy to set up, integrate into Slack, and configure workflows. Since it is integrated into Slack, all of the end users were able to start using it immediately with minimal training. A huge advantage vs a standalone approvals solution”

Andy Chimicles
Head of product at Blade

“Easy to select items necessary for creating work flows and it has a connectivity to other applications which broaden opportunities to make our business flow simple and effective”

Mariko Arai
Senior accountant at Midokura
“Easy to understand and implement with flexibility to adjust your structure. Improve the operation and communication among teams”

Danny L.
Finance manager at Easygo

“We love the way Approveit works within Slack, Its help us streamline our PTO and Expense requests. The support is amazing they seem to respond very quickly and were very helpful with the setup process”

Bobby G.
Executive pastor at Cape Christian
Have Questions?
Have Questions?
Have Questions?
What is BPMA?
BPMA stands for business process management automation. This term is ususlly used in reference to software that is applied to automated complex business processes, leading to improved efficiency, transparency and compliance. Key Components of BPMA: 1. Workflow Automation: automating repetitive tasks and workflows to reduce human error and speed up processes. 2. Process Modeling: using software to map out and design business processes for better understanding and optimization. 3. Data Integration: ensuring seamless data flow between different systems and applications within an organization. 4. Monitoring and Analytics: implementing tools to monitor process performance and analyze data for continuous improvement. 5. Robotic Process Automation (RPA): utilizing software robots to handle high-volume, repeatable tasks that previously required human intervention.
What is BPMA?
BPMA stands for business process management automation. This term is ususlly used in reference to software that is applied to automated complex business processes, leading to improved efficiency, transparency and compliance. Key Components of BPMA: 1. Workflow Automation: automating repetitive tasks and workflows to reduce human error and speed up processes. 2. Process Modeling: using software to map out and design business processes for better understanding and optimization. 3. Data Integration: ensuring seamless data flow between different systems and applications within an organization. 4. Monitoring and Analytics: implementing tools to monitor process performance and analyze data for continuous improvement. 5. Robotic Process Automation (RPA): utilizing software robots to handle high-volume, repeatable tasks that previously required human intervention.
What is BPMA?
BPMA stands for business process management automation. This term is ususlly used in reference to software that is applied to automated complex business processes, leading to improved efficiency, transparency and compliance. Key Components of BPMA: 1. Workflow Automation: automating repetitive tasks and workflows to reduce human error and speed up processes. 2. Process Modeling: using software to map out and design business processes for better understanding and optimization. 3. Data Integration: ensuring seamless data flow between different systems and applications within an organization. 4. Monitoring and Analytics: implementing tools to monitor process performance and analyze data for continuous improvement. 5. Robotic Process Automation (RPA): utilizing software robots to handle high-volume, repeatable tasks that previously required human intervention.
What is the difference between business process management automation (BPMA) and robotic process automation (RPA)?
Business Process Management Automation (BPMA) focuses on the end-to-end management and optimization of entire business processes, involving process modeling, workflow automation, data integration, and performance monitoring (as highlighted in the question above). Robotic Process Automation (RPA), on the other hand, targets the automation of specific, repetitive tasks using software robots that mimic human actions within digital systems. BPMA is more comprehensive and complex, while RPA is task-specific and easier to implement. However, both are very intertwined, so you may see these terms used as interchangeable on the internet.
What is the difference between business process management automation (BPMA) and robotic process automation (RPA)?
Business Process Management Automation (BPMA) focuses on the end-to-end management and optimization of entire business processes, involving process modeling, workflow automation, data integration, and performance monitoring (as highlighted in the question above). Robotic Process Automation (RPA), on the other hand, targets the automation of specific, repetitive tasks using software robots that mimic human actions within digital systems. BPMA is more comprehensive and complex, while RPA is task-specific and easier to implement. However, both are very intertwined, so you may see these terms used as interchangeable on the internet.
What is the difference between business process management automation (BPMA) and robotic process automation (RPA)?
Business Process Management Automation (BPMA) focuses on the end-to-end management and optimization of entire business processes, involving process modeling, workflow automation, data integration, and performance monitoring (as highlighted in the question above). Robotic Process Automation (RPA), on the other hand, targets the automation of specific, repetitive tasks using software robots that mimic human actions within digital systems. BPMA is more comprehensive and complex, while RPA is task-specific and easier to implement. However, both are very intertwined, so you may see these terms used as interchangeable on the internet.
How to automate business processes?
1. Identify processes to automate: Evaluate and prioritize which processes are suitable for automation. Look for repetitive, time-consuming, and error-prone ones. Talk to your team and expore the bottlenecks in your processes together. You might want to implement a special framework for that 2. Define objectives and goals: clearly outline the goals of automation, such as reducing costs, improving speed, or enhancing accuracy; not just in general, bun in the context of specific existing proceses. Set clear business goals that can be quantified. For example: “We’re looking to automate invoice approval process to reduce invoice processing time by 40% and increase accuracy in data entries by 80%”. Establish key performance indicators (KPIs) to measure success. 3. Select the right tools: choose appropriate automation tools based on your needs. Consider factors like scalability, ease of integration, and user-friendliness. Expected RIO should also be a part of your considerations, since for every organization the same SaaS product will provide different ROI. 4. Design and model processes: design the desired workflow. Ensure that the new process model optimizes efficiency and eliminates unnecessary steps. 5. Integrate with existing systems: ensure seamless integration between various systems your team already uses. The more seamless data flow is – the more complete your automation will be. 6. Test automation solutions: explore what benefits each of the competing BPMA systems offers to specifically your business. Test them out and see if features provided work exactly the way you need. 7. Implement and monitor: deploy the automation solution in a controlled environment. Monitor the performance and impact of automation continuously to ensure it meets the set objectives and KPIs. Audit sustem’s performance in different points of your work cycle to see how it handles your processes. Any bottlenecks that appear you can address and eliminate
How to automate business processes?
1. Identify processes to automate: Evaluate and prioritize which processes are suitable for automation. Look for repetitive, time-consuming, and error-prone ones. Talk to your team and expore the bottlenecks in your processes together. You might want to implement a special framework for that 2. Define objectives and goals: clearly outline the goals of automation, such as reducing costs, improving speed, or enhancing accuracy; not just in general, bun in the context of specific existing proceses. Set clear business goals that can be quantified. For example: “We’re looking to automate invoice approval process to reduce invoice processing time by 40% and increase accuracy in data entries by 80%”. Establish key performance indicators (KPIs) to measure success. 3. Select the right tools: choose appropriate automation tools based on your needs. Consider factors like scalability, ease of integration, and user-friendliness. Expected RIO should also be a part of your considerations, since for every organization the same SaaS product will provide different ROI. 4. Design and model processes: design the desired workflow. Ensure that the new process model optimizes efficiency and eliminates unnecessary steps. 5. Integrate with existing systems: ensure seamless integration between various systems your team already uses. The more seamless data flow is – the more complete your automation will be. 6. Test automation solutions: explore what benefits each of the competing BPMA systems offers to specifically your business. Test them out and see if features provided work exactly the way you need. 7. Implement and monitor: deploy the automation solution in a controlled environment. Monitor the performance and impact of automation continuously to ensure it meets the set objectives and KPIs. Audit sustem’s performance in different points of your work cycle to see how it handles your processes. Any bottlenecks that appear you can address and eliminate
How to automate business processes?
1. Identify processes to automate: Evaluate and prioritize which processes are suitable for automation. Look for repetitive, time-consuming, and error-prone ones. Talk to your team and expore the bottlenecks in your processes together. You might want to implement a special framework for that 2. Define objectives and goals: clearly outline the goals of automation, such as reducing costs, improving speed, or enhancing accuracy; not just in general, bun in the context of specific existing proceses. Set clear business goals that can be quantified. For example: “We’re looking to automate invoice approval process to reduce invoice processing time by 40% and increase accuracy in data entries by 80%”. Establish key performance indicators (KPIs) to measure success. 3. Select the right tools: choose appropriate automation tools based on your needs. Consider factors like scalability, ease of integration, and user-friendliness. Expected RIO should also be a part of your considerations, since for every organization the same SaaS product will provide different ROI. 4. Design and model processes: design the desired workflow. Ensure that the new process model optimizes efficiency and eliminates unnecessary steps. 5. Integrate with existing systems: ensure seamless integration between various systems your team already uses. The more seamless data flow is – the more complete your automation will be. 6. Test automation solutions: explore what benefits each of the competing BPMA systems offers to specifically your business. Test them out and see if features provided work exactly the way you need. 7. Implement and monitor: deploy the automation solution in a controlled environment. Monitor the performance and impact of automation continuously to ensure it meets the set objectives and KPIs. Audit sustem’s performance in different points of your work cycle to see how it handles your processes. Any bottlenecks that appear you can address and eliminate
Can you automate business processes in startups and small businesses?
The sooner you implement formal automated processes into your day-to-day work, the better you’ll be off when scaling. Growing businesses often overlook the opportunity to automate and manage existing business processes while the scale is still small and as a result accumulate a large technical debt that is resource-draining and hard to pay out. However, you don’t have to jump into complete end-to-end automation right away – it may not meet your current business needs and result in losses rather than gains. Start with automating the most time-consuming processes first, and move on from there. Common first candidates for automation are: • invoice management process • procurement process • payment process • inventory management • marketing approval process • user support
Can you automate business processes in startups and small businesses?
The sooner you implement formal automated processes into your day-to-day work, the better you’ll be off when scaling. Growing businesses often overlook the opportunity to automate and manage existing business processes while the scale is still small and as a result accumulate a large technical debt that is resource-draining and hard to pay out. However, you don’t have to jump into complete end-to-end automation right away – it may not meet your current business needs and result in losses rather than gains. Start with automating the most time-consuming processes first, and move on from there. Common first candidates for automation are: • invoice management process • procurement process • payment process • inventory management • marketing approval process • user support
Can you automate business processes in startups and small businesses?
The sooner you implement formal automated processes into your day-to-day work, the better you’ll be off when scaling. Growing businesses often overlook the opportunity to automate and manage existing business processes while the scale is still small and as a result accumulate a large technical debt that is resource-draining and hard to pay out. However, you don’t have to jump into complete end-to-end automation right away – it may not meet your current business needs and result in losses rather than gains. Start with automating the most time-consuming processes first, and move on from there. Common first candidates for automation are: • invoice management process • procurement process • payment process • inventory management • marketing approval process • user support
What are Business Operations?
Business operations refer to the activities and processes that organizations implement to produce goods or provide services. Basically, it’s a set of actions businesses do to make money. Key aspects of business operations include: 1. Production: This involves the creation of products or services. It includes managing resources such as labor, materials, and equipment to produce goods efficiently. For example, a factory assembling electronics or a restaurant preparing meals. 2. Supply chain management: Coordinating the flow of materials and products from suppliers to customers. This includes procurement of raw materials, inventory management, logistics, and distribution. 3. Sales and marketing: Activities aimed at promoting and selling products or services. This includes market research, marketing strategies, advertising, sales strategies, account management and much more 4. Human Resources: Managing the recruitment, training, development, and welfare of employees. This ensures the organization has a skilled and motivated workforce. Activities include hiring, performance evaluations, employee retention, and compliance with labor laws. 5. Financial management: Planning, organizing, controlling, and monitoring financial resources. This includes budgeting, accounting, financial reporting, investment strategies, and asset management 6. Customer service: Providing support to customers before, during, and after a purchase. This includes handling inquiries, resolving complaints, addressing requests, gathering feedback and ensuring customer retention (reducing churn) 7. IT and technology management: Managing the technology infrastructure and information systems that support business operations. This includes maintaining hardware, software, and networks, ensuring data security, enforcing access policies, and data protection. 8. Compliance and risk management: Ensuring that the business adheres to legal and regulatory requirements. It also involves identifying, assessing, and mitigating risks to protect the organization from potential threats, physical, legal or otherwise.
What are Business Operations?
Business operations refer to the activities and processes that organizations implement to produce goods or provide services. Basically, it’s a set of actions businesses do to make money. Key aspects of business operations include: 1. Production: This involves the creation of products or services. It includes managing resources such as labor, materials, and equipment to produce goods efficiently. For example, a factory assembling electronics or a restaurant preparing meals. 2. Supply chain management: Coordinating the flow of materials and products from suppliers to customers. This includes procurement of raw materials, inventory management, logistics, and distribution. 3. Sales and marketing: Activities aimed at promoting and selling products or services. This includes market research, marketing strategies, advertising, sales strategies, account management and much more 4. Human Resources: Managing the recruitment, training, development, and welfare of employees. This ensures the organization has a skilled and motivated workforce. Activities include hiring, performance evaluations, employee retention, and compliance with labor laws. 5. Financial management: Planning, organizing, controlling, and monitoring financial resources. This includes budgeting, accounting, financial reporting, investment strategies, and asset management 6. Customer service: Providing support to customers before, during, and after a purchase. This includes handling inquiries, resolving complaints, addressing requests, gathering feedback and ensuring customer retention (reducing churn) 7. IT and technology management: Managing the technology infrastructure and information systems that support business operations. This includes maintaining hardware, software, and networks, ensuring data security, enforcing access policies, and data protection. 8. Compliance and risk management: Ensuring that the business adheres to legal and regulatory requirements. It also involves identifying, assessing, and mitigating risks to protect the organization from potential threats, physical, legal or otherwise.
What are Business Operations?
Business operations refer to the activities and processes that organizations implement to produce goods or provide services. Basically, it’s a set of actions businesses do to make money. Key aspects of business operations include: 1. Production: This involves the creation of products or services. It includes managing resources such as labor, materials, and equipment to produce goods efficiently. For example, a factory assembling electronics or a restaurant preparing meals. 2. Supply chain management: Coordinating the flow of materials and products from suppliers to customers. This includes procurement of raw materials, inventory management, logistics, and distribution. 3. Sales and marketing: Activities aimed at promoting and selling products or services. This includes market research, marketing strategies, advertising, sales strategies, account management and much more 4. Human Resources: Managing the recruitment, training, development, and welfare of employees. This ensures the organization has a skilled and motivated workforce. Activities include hiring, performance evaluations, employee retention, and compliance with labor laws. 5. Financial management: Planning, organizing, controlling, and monitoring financial resources. This includes budgeting, accounting, financial reporting, investment strategies, and asset management 6. Customer service: Providing support to customers before, during, and after a purchase. This includes handling inquiries, resolving complaints, addressing requests, gathering feedback and ensuring customer retention (reducing churn) 7. IT and technology management: Managing the technology infrastructure and information systems that support business operations. This includes maintaining hardware, software, and networks, ensuring data security, enforcing access policies, and data protection. 8. Compliance and risk management: Ensuring that the business adheres to legal and regulatory requirements. It also involves identifying, assessing, and mitigating risks to protect the organization from potential threats, physical, legal or otherwise.

Still Have Questions?
Can’t find the answer you’re looking for?
Please chat to our friendly team.


Still Have Questions?
Can’t find the answer you’re looking for?
Please chat to our friendly team.


Still Have Questions?
Can’t find the answer you’re looking for? Please chat to our friendly team.
©2025 All rights reserved. Approveit, Inc.
©2025 All rights reserved. Approveit, Inc.
©2025 All rights reserved. Approveit, Inc.


Connect workflows across your fools and teams


Ensure full compliance with audit-ready logs and governance


Integrate Slack, Microsoft Teams, ERPs, CRMs, and internal systems














